Before understanding what hard links and soft links are, you must have an idea about innodes in Linux Innode is related to hardlinks and softlinks.
What is an Innode in Linux?
Innode is a Unix data structure that stores information about a file or a folder. But innode does not hold the name of the file or a folder but it has a unique id for the file or a folder.
Two or more files can possess the same innode id. Thats how hardlinks and softlinks work. Every hard disk has an innode table that stores the information about the files in it.
By default, there will be enough innodes specific to the disk size to make sure that you won't run out of innodes.
However, if you happen to run out of innodes, even if you have storage space, you won't be able to create new files on that hard disk. You can manually increase the innode numbers using some programs, which is out of the scope of this tutorial.
So when a user tries to access a file, the innode table retrieves the file using its unique id. So whenever a file is created, it is associated with an innode id.
You Might Like: How to Add Sudo users in Linux
You can see the innode number of a file using the following command.
sudo ls -i /etc/passwd
You can find the number of innodes available in your file system using the following command.
sudo df -i
What is a Softlink in Linux?
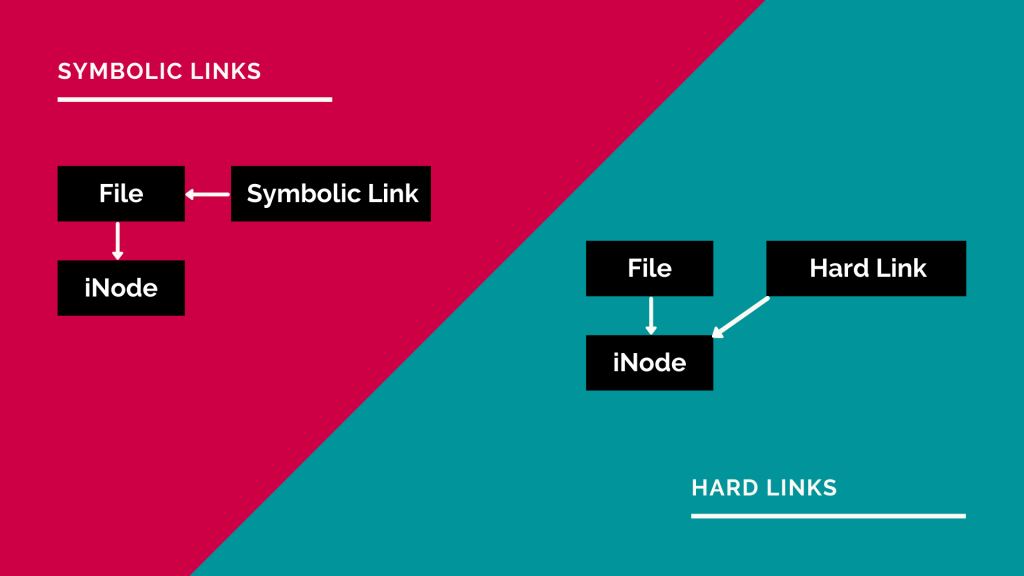
Softlink is like a pointer to a file. Softlink does not create a copy of a file, but instead, it creates a link with the original file in a different name with the same innode entry.
So the original file and the linked file have the same innode entry. If you delete the original file, the link will be lost, and you won't be able to view the files using the softlink or symbolic link, or symlink.
Also, if you move the original file to some other location, you won't be able to read the file using softlink.
Creating A Softlink in Linux
Let's say you have a file named file1 , and you want to access the contents of the file name using some other name called "file2" from a different location; you create a softlink with the file name file2 for file1.
You can have file2 in any other folder. You actually create a link for an original file in a different location. You can create a softlink using the following command.
sudo ln -s ~/demo.text ~/var/www/demo-soft.txt
In the above command, I created a softlink demo-soft.txt in /var/www folder for demo.text present in a root folder. demo.txt is the original file and demo-soft.txt is just a link file that is logically linked to demo.text.
What is a HardLink in Linux?
Hard links create an exact copy of a file with the same innode entry. Both original and hard-linked files will have the same innode id. Unlike softlinks, even if you delete or move the original file, you can access the contents from the linked file.
Creating a Hard Link in Linux
You can create a hard link using the following command.
ln ~/demo.txt ./demo-hard.txt