One of the common questions aspiring DevOps engineers ask is, do we need Python for DevOps? In this blog, we will explain to you why Python is essential in the DevOps world.
Information Technology is not like it used to be before. Most sysadmin tasks are automated using tools and scripting languages, including configuration management tools like Chef, Puppet, Ansible, etc., and scripting languages like shell scripting, python, Ruby, etc.
Also, how people and teams work has changed drastically in recent years with philosophies such as DevOps and methodologies like Agile.
Unlike before, different teams have started working together, and there is more and more automation from application development to deployment. Tools like Vagrant, Docker, and Kubernetes made developers’ lives easy by reducing the time to set up and test development environments.
Cloud computing has drastically changed the way servers are provisioned. You don’t need to wait days to get a server provisioned for your application deployment. With a few clicks, you will have your server ready for deployment.
The process gets easier by writing automation scripts for server provisioning and configuration. One such example is the AWS python boto library. Using Boto SDK, you can automate AWS server provisioning.
What does Python have to do with DevOps?
Gone are the days when DevOps engineers had to work with only CI/CD tools. Nowadays, companies want customized tooling and utilities to fit their CI/CD requirements. A simple example is a Python script to parse JSON to test a functionality in the CI/CD process.
It has led to a shift where people are involved in infrastructure operations, and CI/CD is asked to write custom utilities and modules to improve automation, release, and monitoring.
No company wants to babysit releases and pipelines. However, to develop custom utilities, you should know some level of programming, and the common language preferred in DevOps for such use cases is Python. Arguably Golang is also getting there because most of the modern DevOps tooling is built in Golang.
Also, with more and more MLOPS projects, DevOps engineers have to work with ML engineers, data engineers, and data scientists. Python is a common language among all these teams. As a DevOps engineer, you will be responsible for writing small utility and ML pipeline scripts.
So programming has become necessary for DevOps engineers, and Python is a great language. Also, the need for programming is well explained in this comprehensive DevOps engineers guide.
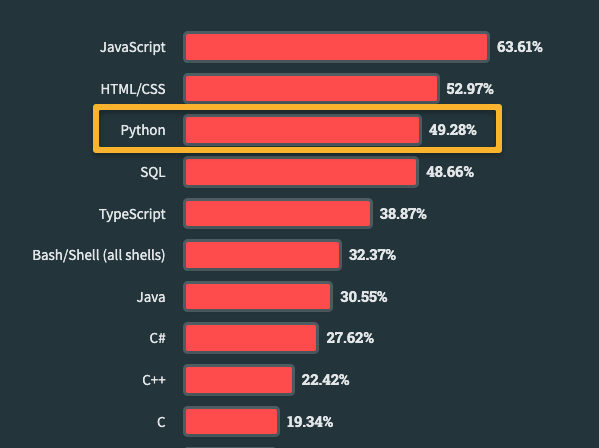
According to the latest StackOverflow Developer Survey, 49.28% of developers prefer Python for scripting.
Why Python For DevOps is Important?
Following are some of the main reasons why Python of DevOps is important
- Python is one of the best scripting languages. The vast availability of Python libraries allows you to write scripts that can communicate with system internals, manipulate files and strings, manage networks, and so on.
- Once you learn Python, you can write automation scripts in a well-structured way. Moreover, every Linux system today comes bundled with Python.
- Many DevOps teams use Python for building custom utilities, web apps for custom data visualization, and more. The main reason is that it’s easy to learn, and you can develop utilities in days rather than months.
- Besides, tools like Ansible are purely written in Python. You can develop custom Ansible modules for your automation tasks. Also, it is not limited to just Ansible; many tools written in Python let you create custom scripts to work with them better.
- Most importantly, during DevOps interviews, you would be asked to solve programming or scripting challenges as part of the first round. Python is the best choice to clear those interview rounds.
So, there are enough reasons why you should learn Python to automate manual tasks.
Python Courses To Skill up in DevOps
If you are completely new to Python, we suggest you go through a guided online course or a book to understand Python fundamentals.
Following are the suggested courses to get started with Python for absolute beginners. These are guided courses with extensive coverage of Python concepts.
Python Scripting Tutorial for Beginners
The first step to getting started with Python is to learn the basics that are needed for scripting. Here we are not going to cover Python for application development but for automation.
In this knowledge base, we will cover a set of articles that will have necessary beginner tutorials to get you started with Python scripting. Following is the list. Subscribe to our mailing list for updates on the following tutorials.
- How to run a Python Script
- Python Basics and Flow Control
- Python Functions
- Lists, Dictionaries, and Structuring Data
- String manipulation and Regular expressions
- Working with Files
- Python Exception handling
- Debugging python scripts
- Working with Linux system configuration.
- Monitoring alerts using python
- System health checks using python
- Managing cron using Python.
- Using Python Modules (Very Important concept to learn)
Python Libraries for DevOps
When it comes to automation using Python, there are many Python libraries that you can make use of. Following are the important Python devops libraries you should look at.
- OS Module
- Subprocess
- JSON
- urlib3
- HTTP
- Kubernetes Python Client
- StatsD
- GitPython
- Requests
- Scapy
- pytest
- Testinfra
- Jinja2
- PyYAML
- Graypy
- Paramiko
- Fabric
Following are the modules related to the three popular cloud providers.
- Boto3 – For AWS services.
- google-cloud-python – For Google Cloud services.
- azure-sdk-for-python – For Microsoft Azure services.
Python Scripts for Automation – DevOps Tasks
To learn Python for DevOps automation, you need to do real-world Python automation tasks. Following is a list of real-world Python scripting use cases.
Here are 50 Python real world DevOps tasks to make your learning better.
- Parse a JSON file: Use
jsonmodule to load and parse JSON data. - Make an HTTP API call with a bearer token: Use
requestslibrary to send authenticated API requests. - Execute SQL statements on PostgreSQL: Use
psycopg2to connect to PostgreSQL and run queries. - Create an EC2 instance using Python boto3: Use
boto3to interact with AWS and launch EC2 instances. - Parse an IP address: Use
ipaddressmodule to validate and manipulate IP addresses. - Segregate IP addresses from a CIDR range: Use
ipaddressto manage IP ranges and extract addresses. - Retrieve Linux system details: Use
psutilto get CPU, memory, disk space, and process information. - Execute a shell script from Python: Use
subprocessto run shell commands and scripts. - Install Nginx in Linux using Python: Automate Nginx installation with
subprocessorosmodule. - Replace a string in a configuration file: Use
fileinputandreto search and replace text. - Retrieve AWS EMR master IP address: Use
boto3to get details of EMR clusters and extract the master node IP. - List all Kubernetes pods in a namespace: Use
kuberneteslibrary to interact with the cluster and list pods. - Automate Docker container management: Use
dockerlibrary to create, start, and stop containers. - Monitor system logs: Read and analyze log files using
loggingmodule or external libraries. - Manage AWS S3 buckets and objects: Use
boto3for creating, listing, and deleting S3 buckets and objects. - Automate software installation and updates: Use scripts to automate package installation and updates.
- Schedule cron jobs using Python: Use
croniterandosto create and manage cron jobs. - Integrate with CI/CD pipelines: Use libraries to interact with CI/CD tools like Jenkins or GitLab.
- Generate and send email notifications: Use
smtplibto send emails based on specific events. - Implement basic network monitoring: Use
psutilor external libraries to monitor network interfaces and traffic. - Manage SSH connections and execute remote commands: Use
paramikoto manage SSH sessions. - Create and manage virtual machines: Use libraries to interact with virtualization platforms like VMware or VirtualBox.
- Automate backup and restore processes: Write scripts to back up data to secure locations and restore it when needed.
- Monitor application performance metrics: Use libraries to collect and analyze application performance data.
- Implement configuration management: Use tools like Ansible and integrate them with Python scripts.
- Automate cloud resource provisioning: Use cloud SDKs to automate the setup of cloud resources.
- Deploy applications to Kubernetes: Use the Kubernetes API to automate application deployments.
- Manage DNS records: Use libraries to interact with DNS providers and manage records.
- Automate firewall configurations: Write scripts to configure firewalls on servers or cloud providers.
- Create custom monitoring dashboards: Use libraries like
matplotliborplotlyto visualize data. - Automate TLS/SSL certificate renewal: Use
certbotto manage and renew certificates from Let’s Encrypt. - Perform automated database backups: Write scripts to regularly back up databases and store them securely.
- Implement log rotation: Use tools like
logrotateand automate it with scripts. - Monitor and scale cloud infrastructure: Write scripts to monitor resource usage and scale cloud resources as needed.
- Manage Kubernetes secrets: Use the Kubernetes API to securely manage sensitive data.
- Automate infrastructure testing: Use testing libraries to validate infrastructure configurations and deployments.
- Parse and analyze logs for error patterns: Write scripts to read log files and identify common error patterns.
- Monitor website uptime and response times: Use libraries to periodically check website status and notify on issues.
- Implement blue-green deployment strategies: Automate the deployment process to ensure zero downtime.
- Set up a Python-based alerting system: Use libraries to monitor systems and send alerts based on specific conditions.
- Automate code linting and formatting: Integrate tools like
flake8orblackto maintain code quality. - Manage IAM roles and policies in AWS: Use
boto3to handle AWS IAM roles and permissions. - Implement security scanning for containers: Use tools to scan container images for vulnerabilities.
- Automate incident response: Write scripts to automate response actions based on monitoring alerts.
- Generate and manage SSH key pairs: Use libraries to create and distribute SSH keys securely.
- Create custom AWS CloudFormation stacks: Use
boto3to automate the creation and management of CloudFormation stacks. - Manage Redis or Memcached instances: Use libraries to connect to and manage these caching systems.
- Implement a webhook listener for GitHub events: Use frameworks to create webhooks and handle GitHub events.
- Automate health checks for services: Write scripts to perform periodic health checks on services and applications.
- Create a self-healing infrastructure setup: Use monitoring and automation tools to detect and fix infrastructure issues automatically.
The list will grow with more examples.
Learn Python By Building Web Apps
The best way for DevOps engineers to learn Python is by building applications.
So how to get started?
You can start with a simple Python micro-framework like Flask to understand how web applications work.
While building an application, you will learn about the front end ( UI ), backend ( middleware/ database connectivity, etc.), and some aspects of development that are helpful for devops engineers in their journey towards becoming one!
It might seem overwhelming initially, but once you finish the tutorial, you will gain some confidence in developing apps.
Following are some of the resources to get started.
- Python Flask tutorial: Build your first Flask application.
- Flask: Develop Web Applications in Python
- Learn the Flask Python Web Development Framework by Building an Ecommerce Platform
Python Alternative for DevOps
One of the best alternatives for Python in DevOps is Golang. Most of the DevOps tools today are built using Golang. For example, Kubernetes, Terraform, and Docker are built using Golang.
Companies that build internal developer portals choose Golang for most of the tooling. Because the existing DevOps tools written in Golang can be easily extended for customization.
Conclusion
This guide covered why using Python for DevOps is essential for a DevOps engineer. The best way to start your DevOps journey is by learning to develop applications. If you know Python basics, you can start with a framework like a Python flask to understand the application workflow.
Also, If you are a DevOps engineer and interested in Kubernetes certification, check out our comprehensive certified Kubernetes administrator exam guide.


Python