DaemonSet is a very important topic in CKA certification.
In this blog, we will learn about a basic understanding of Kubernetes DaemonSets and how to create DaemonSets on Kubernetes.
What is DaemonSets?
DaemonSet is an object of Kubernetes, which is deployed in every cluster node. When a pod is deployed as a DaemonSet, the pod deploys a copy of it in every available node in the cluster.
Also, you cannot increase the number of DaemonSet Pods on a single node since only one can run there.
However, if a DaemonSet Pod is removed from a node, the DaemonSet controller will detect the change and create a new Pod to replace it.
Common Use Cases
Some typical examples of DaemonSets include:
- kube-proxy: manages network rules on each node.
- Cluster Monitoring: tracks node metrics similar to Prometheus Node Exporter.
- logging agents: like Fluentd, Filebeat, or Logstash.
- CNI plugins: such as Calico etc.
You can list the available DaemonSets in your cluster using the following command
kubectl get daemonset -AThis command will list the available DaemonSets on all namespaces as shown below
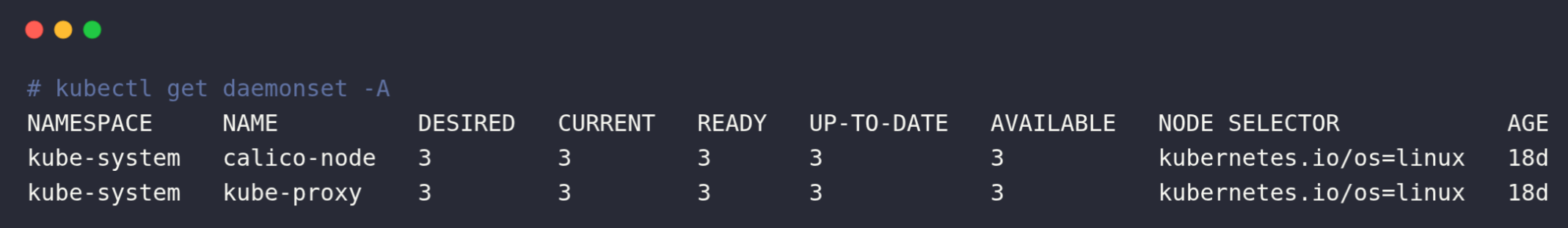
And if you want to list the nodes the DaemonSet pod is running on, run the following command
kubectl get pods -l k8s-app=kube-proxy -o wide -n kube-systemThis command will list the nodes in which the DaemonSet pod kube-proxy is running as shown below
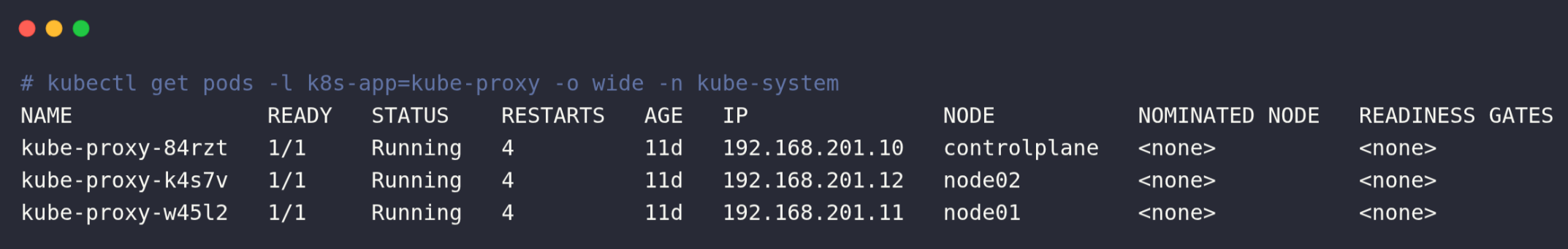
How to Create DaemonSet
Let’s create a simple DaemonSet that deploys an NGINX container on every node
Step 1: Create a manifest file
First, create a manifest file named daemonset.yaml and copy the content provided below:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: nginx-daemonset
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-container
image: nginx:latest
This file will deploy a DaemonSet of Nginx on the default namespace on all available nodes.
Step 2: Apply the DaemonSet
Run the following command to deploy the DaemonSet:
kubectl apply -f daemonset.yamlStep 3: Verify the Deployment
Once it is deployed you can verify if it's deployed as DaemonSet using the command:
kubectl get daemonsets
kubectl get po -o wide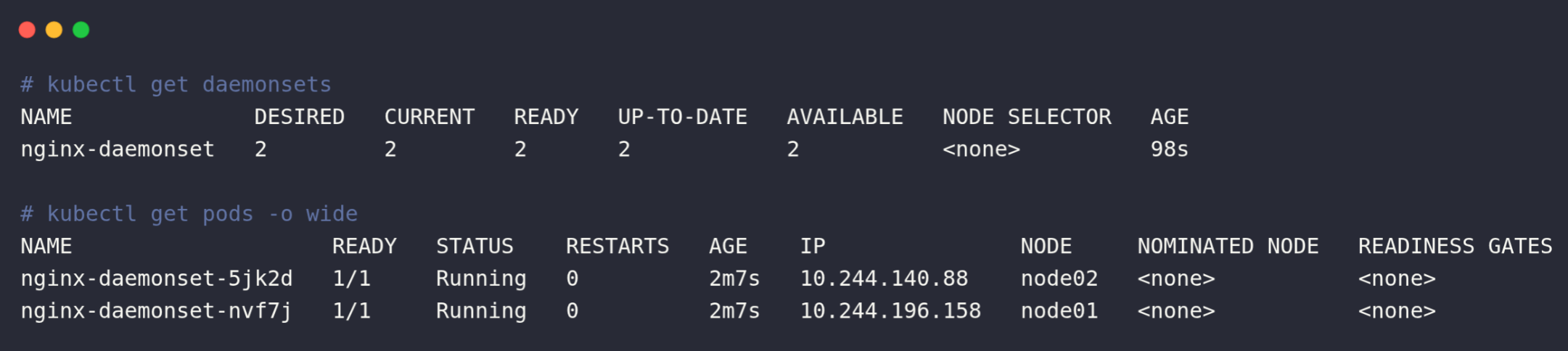
Cleaning Up
To delete the DaemonSet and all its Pods:
kubectl delete daemonset nginx-daemonsetImportant Notes for the CKA Exam
DaemonSets run one Pod per node by default. When a node joins, the DaemonSet automatically deploys the Pod there. When a node leaves, its DaemonSet Pod is automatically removed.
Conclusion
In summary, we have learned about DaemonSets and how to create one.
I believe this blog gives you a basic understanding of DaemonSets.

