In this blog, we will gain a basic understanding of Kubernetes Init Containers and learn how to create one on Kubernetes.
What is Init Containers?
Init containers are containers that start and run before the main container of the pod starts running. Init containers run tasks that are required for the main container to run.
For example, if you have a Java application running in a pod, the purpose of the init containers is to set up the pod for the application to run like configuring the required dependencies for the Java application.
For more clarification, imagine you bought an unfurnished apartment before moving into the apartment. Your initial task is to clean the apartment and set up furniture.
Just like how you won't move into your apartment without cleaning or installing the furniture, the main container wouldn't be able to run the application without the proper environment set by init containers.
How to Create Init Containers
First, create a manifest file init.yaml and copy the content given below
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
initContainers:
- name: init-container
image: busybox
command: ['sh', '-c', 'echo "Simple Init Container Example" > /nginx-init/index.html']
volumeMounts:
- name: nginx-config
mountPath: /nginx-init
containers:
- name: main-container
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: nginx-config
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
volumes:
- name: nginx-config
emptyDir: {}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 30080
This file creates a pod nginx in the default namespace.
Once the pod has been created the init container echos the command to the index.html file.
When the init container completes its task, the main container which has the nginx web server image runs the Nginx web server with the file index.html and shows the content on its web page.
Run the following command to deploy the pod
kubectl apply -f init.yamlOnce you run the command, you can see the pod runs the init container first and then runs the Nginx container as shown below.
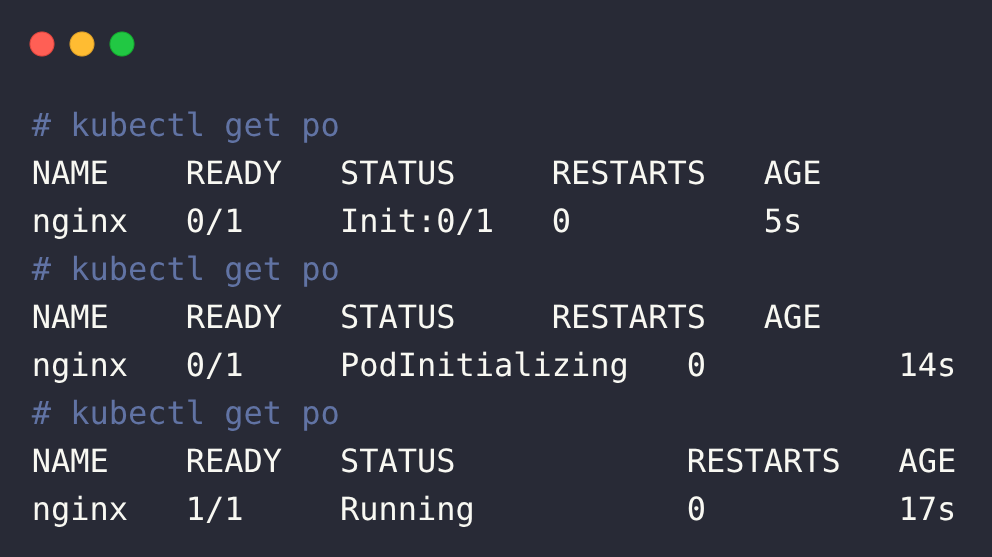
Now the nginx pod is running. Verify that the pod uses the customized index.html file by using Node’s IP address.
Open a web browser and navigate to:
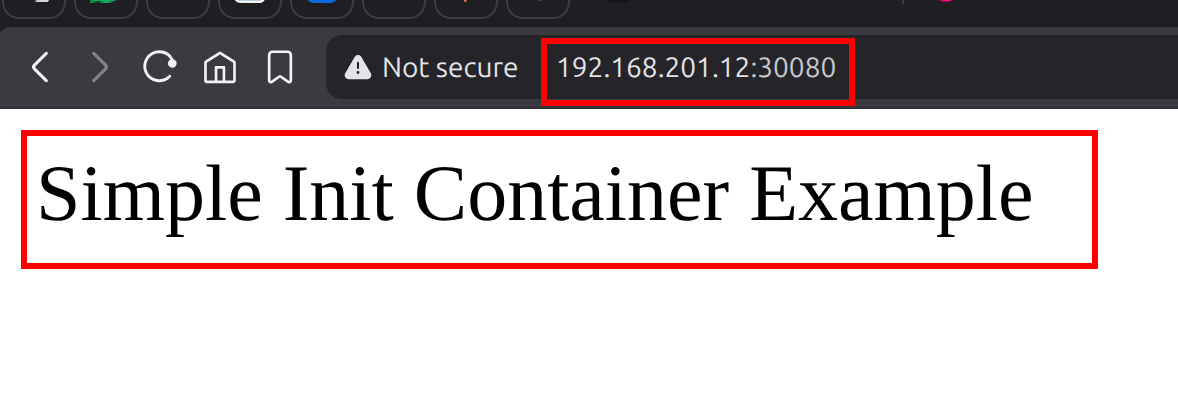
http://<NodeIP>:30080Replace <NodeIP> with the IP address of your Kubernetes node (or control plane) where the service is exposed.
You will get the following output on http://<NodeIP>:30080
Conclusion
In summary, we have learned about init containers and how to create one.
I believe this blog gives you a basic understanding of init containers.