In this blog, we will see how to create Jobs and CronJobs on Kubernetes.
Do you know what is Jobs and CronJobs on Kubernetes?
If you don't know don't worry I will give you a quick review of Jobs and CronJobs in Kubernetes.
What Are Kubernetes Jobs?
Jobs are objects in Kubernetes that deploy a pod, run tasks to completion, and then stop. They do not run continuously like other Kubernetes objects.
Use cases:
- One-time tasks
- Batch data processing
- Database migrations
- Cleanup operations
First, here's a simple example of how to create Jobs on Kubernetes.
Create Jobs
To create a Job, first, create a manifest file job.yaml and copy the below content into it
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: job
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: container
image: busybox
command: ["echo", "Hello, Kubernetes!"]
restartPolicy: NeverRun the following command to create a Job:
kubectl apply -f job.yaml This will create a Job in the default namespace that runs the echo command on the busybox container and then gets terminated.
Check the Job:
kubectl get jobs
Check the logs:
kubectl get pods
kubectl logs <pod-name>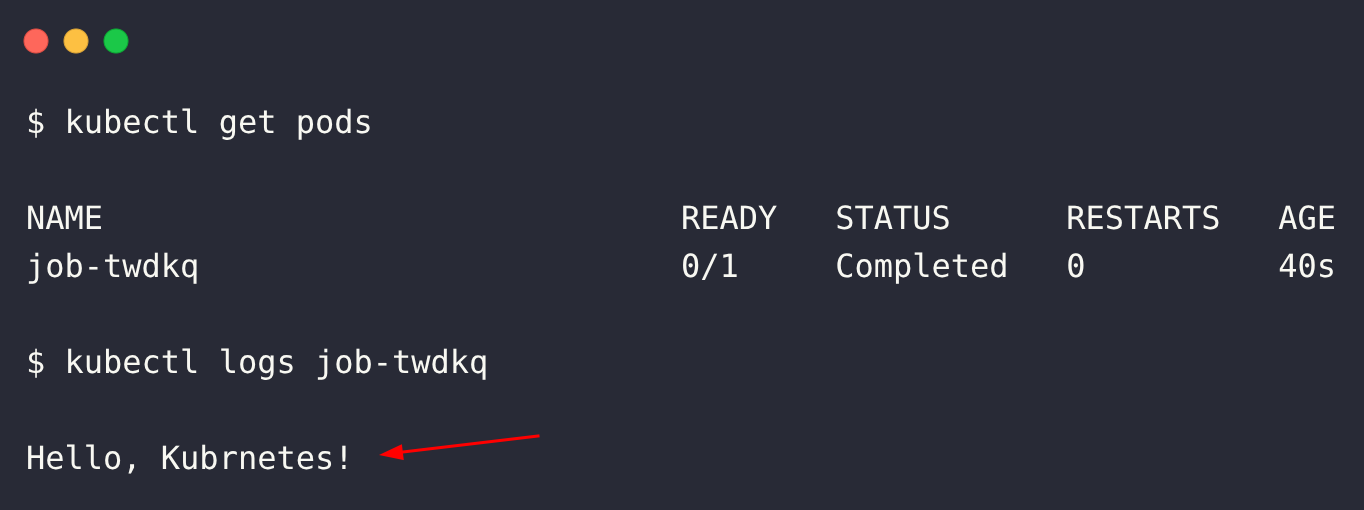
What Are Kubernetes CronJobs?
CronJobs are also a Kubernetes object that schedules tasks to run at specified times. The job will automatically start according to the schedule specified in the job.
Use cases:
- Backups
- Log rotation
- Cleanup jobs
- Scheduled reports
Create CronJobs
Now, let's see how to create CronJobs on Kubernetes.
To create a Job, first, create a manifest file cronjob.yaml and copy the below content into it
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: cronjob
spec:
schedule: "*/1 * * * *"
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: container
image: busybox
command: ["echo", "Hello, Kubernetes!"]
restartPolicy: NeverRun the following command to create a Job:
kubectl apply -f cronjob.yaml This will create a CronJob on the default namespace which schedules the command to run every 1 minute and print “Hello, Kubernetes!”
Check CronJob activity:
kubectl get cronjobs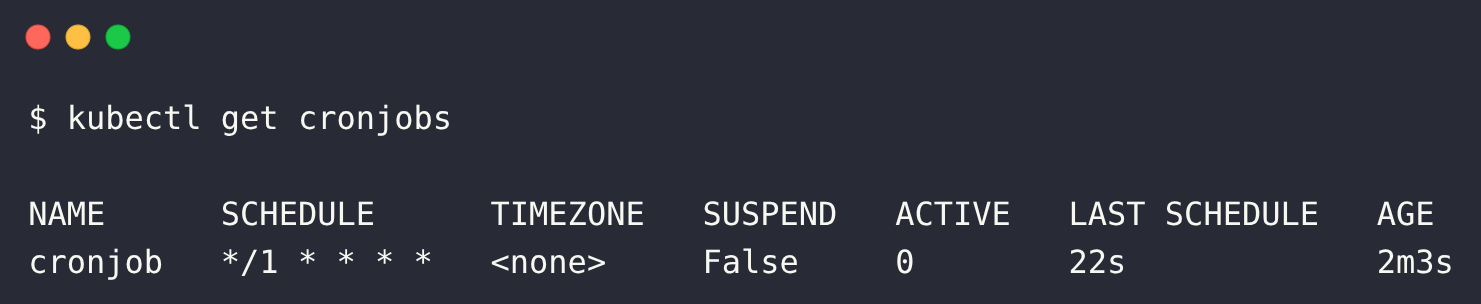
kubectl get jobs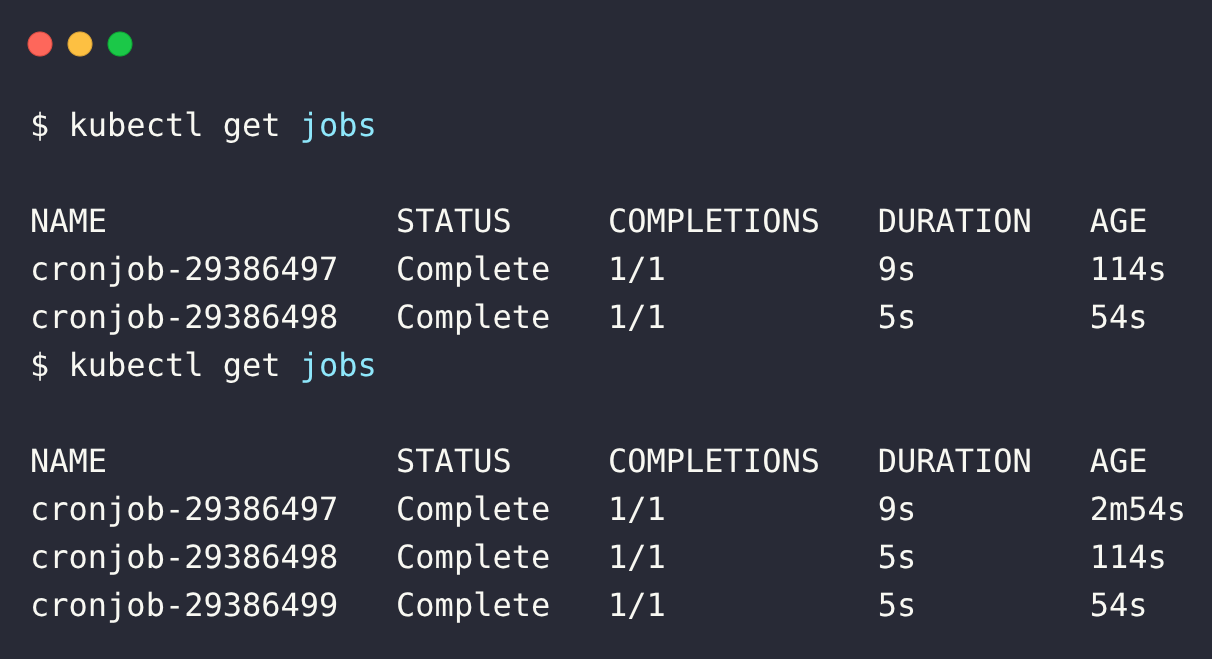
Check the logs:
kubectl get pods
kubectl logs <pod-name>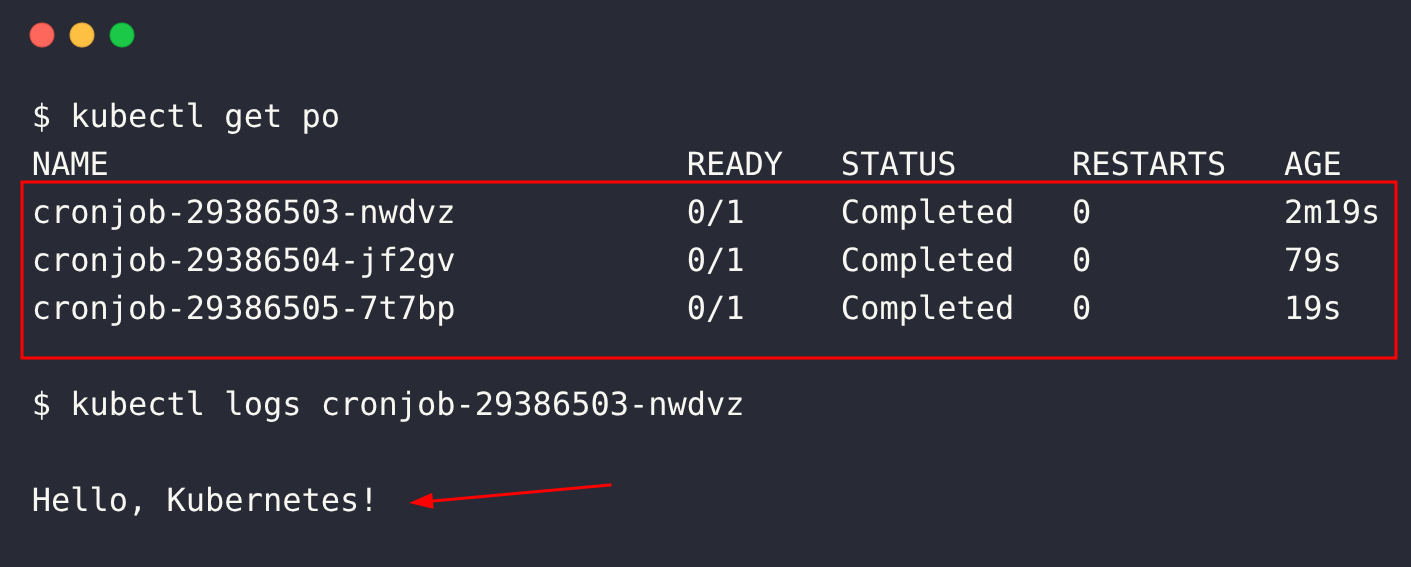
Important Fields for CKA
These fields often appear in exam scenarios.
Jobs:
completions: how many times the Job must run successfullyparallelism: how many Pods run at the same timebackoffLimit: retry count before marking the Job as failed
CronJobs:
suspend: trueto pause CronJobsconcurrencyPolicy:Allow(default)Forbid(do not run new Job if previous is still running)Replace(kill old Job and run a new one)
Conclusion
In this blog, you have learned about how to create Jobs and CronJobs and how they run tasks on Kubernetes.
I hope this blog gives a basic understanding of Kubernetes Jobs and CronJobs.

