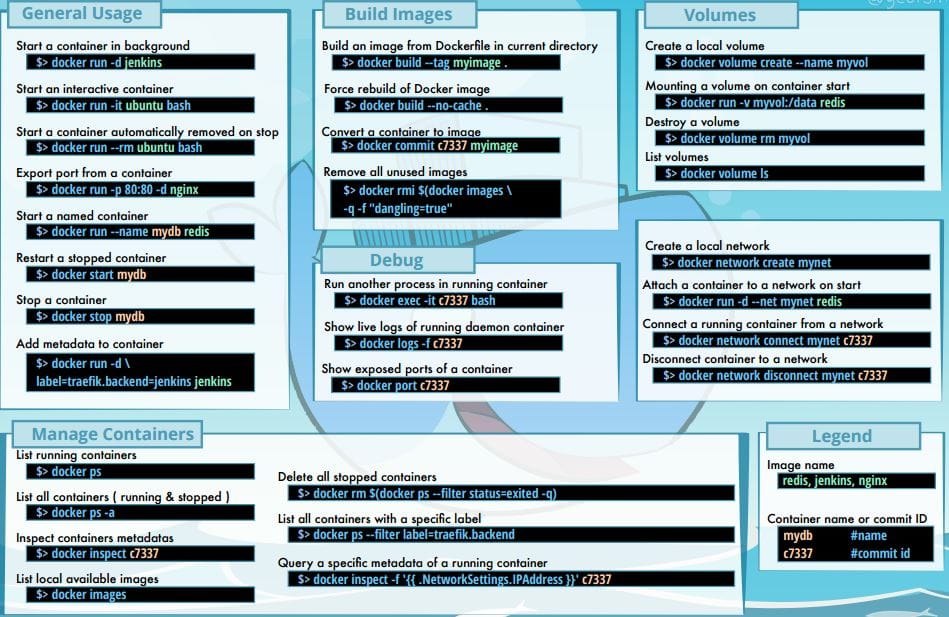
Docker has many commands to remember. If you are starting up with docker, We are pretty sure that you will have a hard time remembering all those commands and to manage containers. In this article, we have explained the necessary command to make you more productive while working with docker.
Docker Useful Hacks
The following section contains useful hacks that help you while working with docker. We don't recommend using the bulk stopping and removing commands in production. This is just for dev purposes.
Run docker without sudo
When you install docker, you have to use sudo to work with docker commands. To avoid using sudo, you need to add your current user to docker group using the following command. Restart the terminal for the changes to take place
usermod -aG docker ${USER}
Execute the following command if you do not want to restart the terminal
newgrp docker
Connecting to Docker Container
Use "docker exec" command to connect to a running container. This command will attach a shell session in your current terminal.
docker exec -it <container-name> bash docker exec -it <container-name> sh
Remove Unused Docker Objects
The best way to remove all stopped, dangling and unused networks is through prune command.
docker system pruneYou can remove all unused docker volumes using volume prune command.
docker system prune --volumesStopping all containers at once
docker stop $(docker ps -a -q)
To forcefully stop,
docker stop -f $(docker ps -a -q)
Removing all containers at once
docker rm $(docker ps -a -q)To forcefully remove,
docker rm -f $(docker ps -a -q)Removing all docker images at once
docker rmi $(docker images -q)To forcefully remove,
docker rmi -f $(docker images -q)Assign a name to the container
To assign a name to a container, use the "--name" parameter as shown below.
docker run -d --name <name-of-container> ubuntu/apacheList all running containers
To list all the running containers, you can use the docker ps command
docker ps
List all containers
To list all running, stopped and exited containers, you can use the -a flag.
docker ps -a
List all images
To list all the available docker images in your host, use the following command.
docker images
Remove unwanted/intermediate/untagged images
Most of the times while building new images, there is a possibility of untagged, intermediate images that might eat up your disk space as well as increases your images list. To clean up those images, you can use the following command.
docker rmi $(docker images --filter "dangling=true" -q --no-trunc)